Bellows Suction Cups FSG (2.5 Folds)
- Diameter: 3 to 32 mm
- Material: HT1, NBR, NBR-CO, NBR-ESD, SI, SI-CO
- Connection nipple plugged into elastomer part
- Conductive, dissipative and mark-free variants
The increasing miniaturization of components, for example in the semiconductor and optical industries, and the constantly growing demands on their precision and reliability make it necessary to control the purity of the working environment, especially in production. This is because only production in a clean working environment makes it possible to carry out and control purity-critical processes. This is why cleanroom technology is being used in more and more industrial sectors.
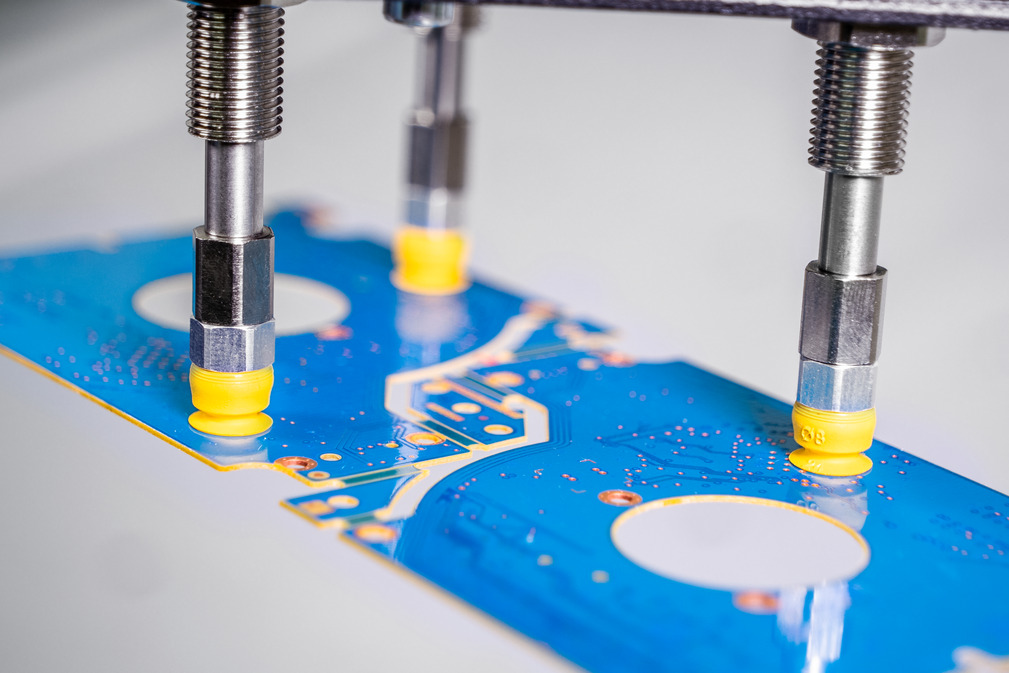
Constantly increasing demands on quality and continuous miniaturization bring challenges in the production and assembly of electronic components. The smallest impurities can have an impact on the function of the end product. Cleanrooms are standard in many manufacturing processes in the semiconductor industry. In the printed circuit board segment, cleanrooms are increasingly used to meet quality requirements. Particular attention must be paid to cleanliness in the assembly processes of the end products.
The automotive industry with its closely networked supplier industry deals with all aspects of the motor vehicle market, from design to production and distribution.
In this industry, cleanrooms enable safe production and high quality standards. Particularly for components of complex systems, such as headlights or speedometers, special requirements for contamination control are necessary and are covered by the cleanrooms.
In the glass industry, various coating processes are used to modify glasses in terms of optical and/or physical properties. To ensure very good coating quality, the upstream and downstream processes already take place in cleanrooms. In the production of laminated safety glass, the films and glass layers are also applied in a cleanroom before the prelaminate is formed.
Cleanrooms are of central importance in display manufacturing. From the production of substrates to the extremely sensitive manufacturing of displays in the various coating processes to module production as well as module assembly, the process takes place in different cleanrooms. The assembly of the actual displays, where the modules are mounted together with electronic components in the housing, also takes place in the cleanroom.
Composite textiles and their processing place high demands on contamination control. Cleanrooms are used in the automotive industry and especially in the aerospace sector and the associated component manufacturing processes. Due to the very high quality requirements in the area of processing raw as well as semi-finished materials with sensitive surfaces and through the use of resins, they are an essential part of the production chain.
To prevent contamination by foreign particles during electrode production, this process takes place in a cleanroom. The cell assembly that follows then even requires a dry room, as otherwise water could lead to chemical reactions inside the cell.
In the food sector, production must take place under hygienically safe conditions. By specifically manufacturing the products and their packaging in the cleanroom, potential hygiene problems are avoided. This leads to a reduction in the total germ count and thus extends the shelf life of the product. Other positive aspects include less wear and tear and fewer machine breakdowns in the production of fresh food.
Fresh products are a good example: Unlike frozen food, the shelf life of fresh products from the refrigerated shelf is limited to a few days to weeks. If the ready meals, salads and pasta specialties are produced and packaged in a cleanroom under low-germ conditions, the shelf life can be extended by up to 50 percent.
In the solar industry, silicon wafers are largely produced in cleanrooms. Especially after the etching and cleaning processes, impurities would significantly reduce the efficiency of the cells. Especially during the necessary surface treatments during solar wafer production, unwanted impurities must be avoided to ensure quality and efficiency class.
Strict hygiene concepts in production and the GMP guidelines (Good Manufacturing Practice) determine the manufacture of pharmaceutical products. The use of cleanrooms in production and packaging helps to meet the high standards. Constant quality controls ensure that no impurities are introduced into sensitive production. For this reason, the use of cleanrooms has become common standard in the pharmaceutical sector.
Cleanroom in the industry
More information on cleanroom in the industry, basics of clean room technology, test procedure for checking cleanroom suitability, suitable products for use in the cleanroom and the certification of Fraunhofer.